luteinizing hormone Activity WOMEN
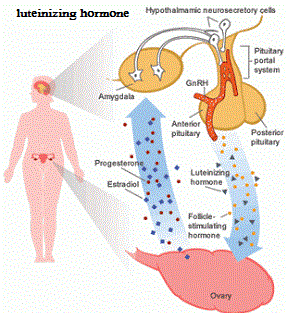 luteinizing hormone In women , LH supports the theca cells of the ovary that provide hormone androgen precursors for the production of estradiol. At the time of menstruation , FSH follicle growth begins , and which affect the granule cells . [ 7 ] With the increase in the hormone estrogen , which is the expression of LH receptors in mature follicles also , which leads to an increased production of estradiol. Finally , when the follicles were fully ripened , and an increase in production of 17 - hydroxy - follicles progesterone inhibits the estrogen production, which leads to a reduction in estrogen -mediated adverse effects of GnRH in the hypothalamus , which in turn stimulates the release of LH from anterior pituitary . This increased production of LH only takes 24 to 48 hours . This "boom LH " is called ovulation , and therefore not only the release of the ovum from the follicle , but also tried to rotate the pores remaining in the corpus luteum , which , in turn , produces progesterone for prepare the endometrium for possible implantation. LH is necessary to maintain the function of the corpus luteum for the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle. in the case of pregnancy , and LH levels fall, and instead remain luteal function HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin , a hormone LH is very similar to , but secreted by the placenta again
luteinizing hormone In women , LH supports the theca cells of the ovary that provide hormone androgen precursors for the production of estradiol. At the time of menstruation , FSH follicle growth begins , and which affect the granule cells . [ 7 ] With the increase in the hormone estrogen , which is the expression of LH receptors in mature follicles also , which leads to an increased production of estradiol. Finally , when the follicles were fully ripened , and an increase in production of 17 - hydroxy - follicles progesterone inhibits the estrogen production, which leads to a reduction in estrogen -mediated adverse effects of GnRH in the hypothalamus , which in turn stimulates the release of LH from anterior pituitary . This increased production of LH only takes 24 to 48 hours . This "boom LH " is called ovulation , and therefore not only the release of the ovum from the follicle , but also tried to rotate the pores remaining in the corpus luteum , which , in turn , produces progesterone for prepare the endometrium for possible implantation. LH is necessary to maintain the function of the corpus luteum for the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle. in the case of pregnancy , and LH levels fall, and instead remain luteal function HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin , a hormone LH is very similar to , but secreted by the placenta againluteinizing hormone Activity men
In men , LH works in the Leydig cells of the testes and regulated by LH. [ 8 ] the testosterone producing Leydig cells (T ) under the control of LH, which regulates expression of the enzyme β - 17 hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase , which is used for the conversion of androstenedione , the luteinizing hormone produced by the gonads , testosterone, [9] and androgens may engage in any activity and the endocrine system in the formation of testicular sperm .
LH released from the pituitary gland , and is controlled by pulses of gonadotropin secretion (GnRH ) . When G levels are low, which is released from the hypothalamus and pituitary GnRH to stimulate the release of LH . [ 10 ] As the rates increase T, and take place in the hypothalamus and pituitary and negative feedback by inhibiting the release of GnRH and LH therefore . [11] However, T must taste of estradiol (E2 ) to stop the LH . E2 reduces the amplitude of the pulse and the response of GnRH by hypothalamic pituitary . [ 12 ]
luteinizing hormoneAnd changes in levels of ( G ) and the pulse discharge of blood by the variations of the human male libido in LH and testosterone
luteinizing hormone
0 التعليقات:
إرسال تعليق